Syrian Army
| Syrian Army | |
|---|---|
| الْجَيْشُ الْعَرَبيُّ السُّورِيُّ | |
 Syrian Arab Army Flag | |
| Founded | 1 August 1945[1] 1971 (current form) |
| Country | |
| Type | Army |
| Role | Land warfare |
| Size | 130,000[2]
Military age: 18 Conscription: |
| Part of | |
| Garrison/HQ | Damascus |
| Motto(s) | "Arabic: حُمَاةَ الدِّيَارِ" (Guardians of the Homeland) |
| Colors |
|
| Anniversaries | August 1st |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| President of Syria | Marshal Bashar al-Assad |
| Minister of Defense | Gen. Ali Mahmoud Abbas |
| Chief of the General Staff | Gen. Abdul Karim Mahmoud Ibrahim |
The Syrian Army (SyA or SA), officially the Syrian Arab Army (SyAA or SAA) (Arabic: الْجَيْشُ الْعَرَبيُّ السُّورِيُّ, romanized: al-Jayš al-ʿArabī as-Sūrī), is the land force branch of the Syrian Armed Forces. It is the dominant military service of the four uniformed services, controlling the most senior posts in the armed forces, and has the greatest manpower, approximately 80 percent of the combined services. The Syrian Army originated in local military forces formed by the French after World War I, after France obtained a mandate over the region.[5] It officially came into being in 1945, before Syria obtained full independence the following year.
Since 1946, it has played a major role in Syria's governance, mounting six military coups: two in 1949, including the March 1949 Syrian coup d'état and the August 1949 coup by Colonel Sami al-Hinnawi, and one each in 1951, 1954, 1963, 1966, and 1970. It has fought four wars with Israel (1948, the Six-Day War in 1967, the Yom Kippur War of 1973, and 1982 Lebanon War) and one with Jordan (Black September in Jordan, 1970). An armored division was also deployed to Saudi Arabia in 1990–91 during the Gulf War, but saw little action. From 1976 to 2005 it was the major pillar of the Syrian occupation of Lebanon. Internally, it played a major part in suppressing the 1979–82 Islamist uprising in Syria, and since early 2011 has been heavily engaged in fighting the Syrian Civil War, the most violent and prolonged war the Syrian Army has taken part in since its establishment in the 1940s.
History[edit]
In 1919, the French formed the Troupes spéciales du Levant as part of the Army of the Levant in the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon. The former with 8,000 men later grew into both the Syrian and Lebanese armies. This force was used primarily as auxiliaries in support of French troops, and senior officer posts were held by Frenchmen, although Syrians were allowed to hold commissions below the rank of major.[6]
1946–1970[edit]
As Syria gained independence in 1946, its leaders envisioned a division-sized army. On June 19, 1947, the Syrian Army took the survivors of Pan Am Flight 121 to the Presbyterian mission hospital at Deir ez-Zor. The 1st Brigade was ready by the time of the Syrian war against Israel on May 15, 1948. It consisted of two infantry battalions and one armored battalion. The 2nd Brigade was organized during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War and also included two infantry battalions and one armored battalion.[7]
At the time of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the army was small, poorly armed, and poorly trained. "Paris had relied primarily on French regulars to keep the peace in Syria and had neglected indigenous forces. Consequently, training was lackadaisical, discipline lax, and staff work almost unheard of. ... there were about 12,000 men in the Syrian army. These troops were mostly grouped into three infantry brigades and an armored force of about battalion size," writes Pollack.[8]
Between 1949 and 1966, a series of military coups destroyed the stability of the government and any remaining professionalism within the army. In March 1949, the chief of staff, General Husni al-Za'im, installed himself as president. Two more military dictators followed by December 1949. General Adib Shishakli then held power until deposed in the 1954 Syrian coup d'etat. Further coups followed, each attended by a purge of the officer corps to remove supporters of the losers from the force.[9] 'Discipline in the army broke down across the board as units and their commanders pledged their allegiance to different groups and parties. Indeed, by the late 1950s, the situation had become so bad that Syrian officers regularly disobeyed the orders of superiors who belonged to different ethnic or political groups.[10]
The 1963 Syrian coup d'état had as one of its key objectives the seizure of the Al-Kiswah military camp, home to the 70th Armored Brigade. In June 1963, Syria took part in the Iraqi military campaign against the Kurds by providing aircraft, armoured vehicles and a force of 6,000 soldiers. Syrian troops crossed the Iraqi border and moved into the Kurdish town of Zakho in pursuit of Barzani's fighters.[11] There was another 1966 Syrian coup d'etat.
However, in 1967 the army did appear to have some strength. It had around 70,000 personnel, roughly 550 tanks and assault guns, 500 APCs, and nearly 300 artillery pieces.[12] The army had sixteen brigades: twelve infantry, two armored (probably including the 70th Armored), and two mechanized. The Syrian government deployed twelve of the sixteen brigades to the Golan, including both armored brigades and one mechanized brigade. Three 'brigade groups', each comprising four brigades, were deployed: the 12th in the north, holding the sector from the B'nat Ya'acov bridge to the slopes of Mount Hermon, the 35th in the south from the B'nat Ya'acov bridge to the Yarmuk River border with Jordan, and the 42nd in reserve, earmarked for a theater-level counterattack role. During the Six-Day War Israeli assault of the Golan heights, the Syrian army failed to counterattack the Israelis as the Israelis breached the Syrian positions. While Syrian units fought hard whenever the Israelis entered their fields of fire, no attempts appear to have been made to exploit Israeli disorientation and confusion during the initial assault.[13]
Judging from reports of 1967–1970, including the reporting of the 5th Infantry Division in 1970, the Army appears to have formed its first divisions during this period. The 1st and 3rd Armored Division, and 5th, 7th, and 9th Mechanized Infantry Divisions were all formed prior to 1973.[14] Samuel M. Katz writes that after Hafez al-Assad gained power in November 1970, the army expanded to the five divisions listed above, plus ten independent brigades, an artillery rocket brigade (the 69th), and "a reinforced brigade variously termed the 70th Armored Brigade or the Assad Republican Guard. It is today known as the Armored Defense Force; as Assad's praetorian guard it is stationed in and around Damascus and subordinate to the Defense Companies under the command of Assad's brother Rifa'at."[15]
1970–2010[edit]
On 18 September 1970, the Syrian government became involved in Black September in Jordan when it sent a reinforced armored brigade to aid the Palestine Liberation Organization.[16] Syrian armored units crossed the border and overran Irbid with the help of local Palestinian forces. They encountered several Jordanian Army detachments, but rebuffed them without major difficulty. Two days later, the 5th Infantry Division, heavily reinforced, was also sent into Jordan. Two armored brigades were attached to the division, bringing its tank strength up to over 300 T-55s and its manpower to over 16,000. The division entered Jordan at ar-Ramtha, destroyed a company of Jordanian Centurion tanks there, and continued directly towards Amman.
Pollack says it is likely that they intended to overthrow the Jordanian monarchy itself. Despite defeating the Jordanian Army at al-Ramtha on 21 September, after fierce air attacks on 22 September, the Syrians stopped the attack and began to retreat.The retreat was caused by Jordan's appeal for international aid : "The report said that Hussein “not only appealed for the moral and diplomatic support of the United Kingdom and the United States, coupled with the threat of international action, but had also asked for an air strike by Israel against Syrian troops.” (New York Post)[17]

After 1970 further Syrian engagements included:
- October War against Israel[18]
- Lebanese Civil War (1975–1990), (against Lebanese militias, the PLO and Israel)
The Syrian armed forces have also been involved in suppressing dissident movements within Syria, for example the Islamist uprising in Syria in 1979–1982. In March 1980 the 3rd Armored Division and detachments from the Defense Companies arrived in Aleppo. The division was under the command of General Shafiq Fayadh, Hafiz Assad's first cousin. The troops sealed "off whole quarters and carr[ied] out house-to-house searches, often preceded by tank fire."[19] Hundreds of suspects were rounded up. Only two conventional Army brigades deployed to Hama in 1982, the 3rd Armored Division's 47th Armored and 21st Mechanized Brigades. Three quarters of the officers and one third of the soldiers in the two brigades were Alawites.[20] Most of the repression was carried out by the Defense Companies and the Special Forces. Meanwhile, the Special Forces were isolating and combing through Hama, killing and capturing suspected government opponents.[21]
Syrian forces fought Israel during the 1982 Lebanon War.
In 1984, Major General Ali Haidar's Special Forces were instrumental in blocking an abortive attempt by Rifaat Assad and his Defense Companies to seize the capital.[22] Fayadh's 3rd Armoured Division moved into the capital to join Haidar's forces in the confrontation with the Defense Companies. The 3rd Armoured Division, it seems, had historically been based at al-Qutayfah, near Damascus.[23]
Bennett dates the establishment of corps in the Syrian Army to 1985. Writing forty years later, Tom Cooper says "..despite the establishment of.. corps.. most division commanders continued reporting directly to the President. Correspondingly, not only the Chief of Staff of the Syrian Armed Forces but also the Corps HQ exercised only a limited operational control over the Army's divisions."[24] Declassified CIA documents from February 1987 say that the 3rd Corps and 17th and 18th Armoured Divisions were established in 1986.[25]

The 9th Armoured Division served in the 1991 Persian Gulf War as the Arab Joint Forces Command North reserve and saw little action.[26]
In 1994, Haidar expressed objections to the Syrian president's decision to bring Bashar home from his studies in Britain and groom him for the succession after the death of Basil, the eldest Assad son.[22] Soon afterwards, on 3 September 1994, Jane's Defence Weekly reported that then-President Hafez Assad had dismissed at least 16 senior military commanders. Among them was Haidar, then commander of the Special Forces, and General Shafiq Fayadh, a cousin of the President who had commanded the "crack" 3rd Armored Division for nearly two decades. The 3rd Armored Division was "deployed around Damascus." JDW commented that "the Special Forces and the 3rd Armored Division, along with the 1st Armored Division are key elements in the security structure that protects Assad's government. Any command changes involving those formations have considerable political significance." Post-uprising reporting indicated the 1st Armored Division had historically been at al-Kiswah.[23]
On 29 September 2004, Jane's Defence Weekly reported that Syria had begun to redeploy elements of one or more Syrian Army special forces regiments based in the coastal hills a few kilometres south of Beirut in Lebanon. A senior Lebanese Army officer told JDW that the 3,000 troops involved would return to Syria.[27]
Cordesman wrote that in 2006 the Syrian Army had "organized two corps that reported to the Land Forces General Staff and the Commander of the Land Force."
As of 2010, the army's formations included three army corps (the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd), eight armored divisions (with one independent armored brigade), three mechanized divisions, one armored-special forces division and ten independent airborne-special forces brigades.[28] The army had 11 divisional formations reported in 2011, with a fall in the number of armored divisions reported from the 2010 edition from eight to seven.[29] The independent armored brigade had been replaced by an independent tank regiment.
In 2009 and 2010, according to the International Institute for Strategic Studies in London, the Syrian army comprised 220,000 regular personnel, and the entire armed forces (including the navy, air force and air defenses) had 325,000 regular troops.[30] Additionally, it had about 290,000 reservists.[30][31][32]
Syrian Civil War[edit]
Military equipment in April 2011 (including storage)[edit]
The vast majority of Syrian military equipment was Soviet manufactured.[33][34]
- ≈ 9,300 armoured fighting vehicles (including in storage):
- ≈ 4,800 main battle tanks
- ≈ 4,500 infantry fighting vehicles and armored personnel carriers
- ≈ 6,400 towed artillery pieces:
- 1,900 guns/howitzers
- ≈ 1,500 anti-aircraft guns
- ≈ 850 self-propelled artillery pieces:
- 2,190+ anti-tank guided weapon launchers
- 500 multiple launch rocket systems
- 84 tactical ballistic missile launchers
- 4,235+ surface-to-air missile launchers:
- 4,000+ MANPADS
- 235 self-propelled air-defense systems
Defections[edit]
At October 1, 2011, according to high-ranking defected Syrian Colonel Riad Assaad, 10,000 soldiers, including high-ranking officers, had deserted the Syrian Army.[35] Some of these defectors had formed the Free Syrian Army, engaging in combat with security forces and soldiers in what would turn into the Syrian Civil War.
At 16 November 2011, Rami Abdel Rahman, the head of the UK-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, however estimated that less than 1,000 soldiers had deserted the Syrian Army; at the same moment, an FSA battalion commander claimed that the FSA embraced 25,000 army deserters.[36] Also in November 2011, the Free Syrian Army or the website of France 24 estimated the Syrian Army at 200,000 troops.[37] According to General Mustafa al-Sheikh, one of the most senior defectors, however, in January 2012 the Syrian forces were estimated at 280,000 including conscripts.[38]
By March 15, 2012, many more soldiers, unhappy with crackdowns on pro-democracy protesters, switched sides and a Turkish official said that 60,000 soldiers had deserted the Syrian army, including 20,000 since February 20. It was added that most of the deserters were junior officers and soldiers.[39] By 5 July 2012, the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights estimated "tens of thousands" soldiers to have defected.[32] By August 2012, 40 Brigadier generals from the Army had defected to the opposition army, out of a total of 1,200 generals.[40]
On June 14, 2013, 73 Syrian Army officers and their families, some 202 people in total, sought refuge in Turkey. Amongst their number were seven generals and 20 colonels.[41] In 2013, Agence France Press wrote on 'Syria's diminished security forces.'[31]
Strength impaired[edit]
Up until July 2012, the scale of defections from the Syrian Army, though hard to quantify, was too small to make an impact on the strength of that army, according to Aram Nerguizian from the Washington-based Center for Strategic and International Studies.[32] Strategically important units of the Syrian armed forces are always controlled by Alawite officers; defecting soldiers – by July 2012 "tens of thousands" according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights – are mainly Sunni without access to vital command and control, Nerguizian said,[32] however the formed Syrian Minister of Defense General Dawoud Rajiha killed in the 18 July 2012 Damascus bombing was a Christian.
The army in Syria is the power structure. The armed forces would fight to an end. It would be a bloodbath, literally, because the army would fight to protect not only the institution of the army but the regime itself, because the army and the regime is one and the same.
— Fawaz Gerges, Lebanese-American author[42]
Analyst Joseph Holliday wrote in 2013 that "the Assad government has from the beginning of the conflict been unable to mobilize all of its forces without risking largescale defections. The single greatest liability that the Assad regime has faced in employing its forces has been the challenge of relying on units to carry out orders to brutalize the opposition."[43] This has resulted in Bashar's following his father's precedent by attaching regular army units to more reliable forces (Special Forces, Republican Guard, or 4th Armored Division). When Hafez al-Assad directed the suppression of revolts in Hama in 1982, this technique was also used.[44]
.jpg/220px-Breaking_siege_of_Nubl_and_Al-Zahraa_(7).jpg)
In 2014, analyst Charles Lister wrote that "As of April 1, 2014, the SAA had incurred at least 35,601 fatalities, which when combined with a reasonable ratio of 3 wounded personnel for every soldier killed and approximately 50,000 defections, suggests the SAA presently commands roughly 125,000 personnel. This loss of manpower is exacerbated by Syria's longentrenched problem of having to selectively deploy forces based on their perceived trustworthiness."[44] The International Institute for Strategic Studies in London calculated that by August 2013 the strength of the Syrian army had, compared with 2010, roughly been cut in half, due to defections, desertions and casualties: it now counted 110,000 troops.[31]
The Syrian Arab Army suffers from serious recruitment issues as the Syrian Civil War drags on, with military age men across sectarian lines no longer willing to join or serve their conscription terms. These issues are especially notable among the Druze population, who have clashed with regime security forces and broken Druze youths out of regime imprisonment to avoid them serving in the army.[45] Increasingly, Assad's Alawite base of support refuse to send their sons to the military due to massive casualty rates among military age men in their community; according to pro oppositions sources a third of 250,000 Alawite men of fighting age have been killed in the Syrian Civil War, leading to major tensions between the sect and the Syrian government.[46]
As of mid-2018, then-Israeli Defence Minister Avigdor Lieberman said that the Syrian Arab Army had regained its pre-2011 strength levels, recovering from manpower shortages earlier in the Syrian Civil War.[47]
Roles of 3rd, 11th, 17th and 18th Divisions[edit]
.jpg/220px-Liberation_of_Palmyra_by_RSII_coalition_(4).jpg)
The 3rd Armored Division has deployed elements of three brigades from its bases around Qutayfah to Deraa, Zabadani, and Hama, while the 11th Armored Division has stayed close to its bases in Homs and Hama.[48]
The European Council named Major General Wajih Mahmud as commander of the 18th Armored Division in the Official Journal of the European Union on 15 November 2011, sanctioning him for violence committed in Homs.[49] Henry Boyd of the IISS noted that "in Homs, the 18th Armored Division was reinforced by Special Forces units and ... by elements of the 4th Division under Maher's de facto command."[50]
Information from Holliday 2013 suggests that the reserve armored division is the 17th (rather than any other designation), which was responsible for eastern Syria.[51] The division's 93rd Brigade left Idlib to secure Raqqa Governorate in early 2012.[52] Following the reported capture of Raqqa on 3–6 March 2013, elements of the 17th Division remained under siege to the north of the city in October 2013.[53]
Relationship with National Defense Force[edit]
The National Defense Force is under the control and supervision of the Syrian Army[54] and acts in an infantry role, directly fighting against rebels on the ground and running counter-insurgency operations in co-ordination with the army which provides them logistical and artillery support.
Struggling with reliability issues and defections, officers of the SAA increasingly prefer the part-time volunteers of the NDF, who they regard as more motivated and loyal, over regular army conscripts to conduct infantry operations and act as support for advancing tanks.[55]
An officer in Homs, who asked not to be identified, said the army was increasingly playing a logistical and directive role, while NDF fighters act as combatants on the ground.[56]
The NDF continues to play a significant role in military operations across Syria despite the formation of other elite units, many of which receive direct assistance from Russia.
4th Corps (2015–2018)[edit]
Two new corps have been established since the civil war began in 2011. In October 2015, the 4th Assault Army Corps (Arabic: 4 فيلق اقتحام) was established in the northeast.[57]
The "4th Corps", "4th Assault Corps",[58] or "4th Volunteer Assault Corps",[citation needed] also called the Fourth Legion - Assault [59] is a new formation of the Syrian Army, organized with Russian help since 2015. The original plan for the 4th Corps was to reorganize the weakened regular army units as well as irregular pro-government militias,[60] including some National Defence Forces (NDF) units,[61] in the governorates of Latakia as well as Tartus, and on the al-Ghab Plain. These forces would be trained, organized and armed by the Russian Armed Forces, so that they could become "special" ground forces which would retake northernwestern Syria with Russian air support.[62]
When the 4th Corps was subsequently organized in summer and fall 2015, forces of widely different origins were included: Among these were the 103rd Republican Guard Brigade which would serve as HQ for the new corps,[citation needed] along with troops drawn from the 3rd and 4th Divisions, as well as Ba'ath Party, NDF, and Alawite militias.[58] The Alawite fighters were organized into 12 units which fought under the joint command of Russian, Syrian, and Iranian officers.[63][60] The remained was grouped into four "volunteer brigades",[citation needed] while several smaller Russian units were assigned to it in a support role.[58] Directly paid by the Republican Guard and the government,[60] the 4th Corps was described by Carnegie Middle East Center's expert Kheder Khaddour a formation that "blends army and militia forces".[63]
Although the 4th Corps' initial operations such as during the 2015–16 Latakia offensive and Northwestern Syria offensive (October–November 2015)[58][64] were relatively successful, the inclusion of more militias into the corps remained elusive. This was probably due to the fact that Iran remained unwilling to allow Syrian units under its control to be integrated to a primarily Russian-led formation, while many militias generally resisted any attempts to reduce their autonomy by including them in the 4th Corps.[61][58] As result, the 4th Corps remained mostly limited to Latakia, where it continues to be active. As its performance during the 2016 Latakia offensive was lacking, however, its overall commander Maj. Gen. Shuqi Yusuf was dismissed in July 2016.[58][65] Overall, the 4th Corps did not "live up to Moscow's expectations" and its Syrian commanders "demonstrated poor performance", despite the fact that the corps had actually succeeded in reforming the included militias into a "disciplined, organized military force".[58]
Gregory Waters wrote via Twitter in November 2018 that "..the 6th Division [was] one of two divisions created under the Russian-built 4th Corps back in 2015. The 4th Corps project largely failed & the 6th & 2nd Divisions have remained in Latakia since."[66]
Demographics[edit]
Sunni and Shia (Alawite) Muslims make up the majority of the Syrian Arab Army and many hold high governmental positions.[67] Religious minorities also serve in the Army, such as Druzes, Christians and Yazidis. From the start of the Syrian Civil War till now, the Syrian Arab Army has been composed mainly of Sunni Syrians (for example, the 4th Mechanized Division is entirely composed and led by Sunnis),[68] with mixed religious leadership at higher military positions.[69]
Since 2022, the Minister of Defense and also Deputy Commander-in-Chief of the Army and the Armed Forces Lieutenant General Ali Mahmoud Abbas, and Major General Mufid Hassan, Deputy Chief of the General Staff, are some of the Sunni Muslims in the positions of power.[70] Some volunteer brigades, such as Arab Nationalist Guard, are made up of Sunni Syrians and other Sunnis from the Middle Eastern region that adhere to pan-Arab ideals.[71]
Structure in 2001[edit]

Before 2011, it was difficult to access reliable information about the SAA because of the Damascus government's sensitivity to potential espionage, particularly by Israel.[72]
Richard Bennett wrote in 2001 that "..corps [were] formed in 1985 to give the Army more flexibility and to improve combat efficiency by decentralizing the command structure, absorbing at least some of the lessons learned during the Israeli invasion of the Lebanon in 1982."[73] The organization and military doctrine of the army followed the Soviet model.[74]
Richard Bennett's estimate of the 2001 order of battle was:
- 1st Corps HQ Damascus, which covered from Golan Heights, the fortified zone and south to Der'a near the Jordanian border.
- 5th Armored Division, which included the 17th and 96th Armored Brigades and the 112th Mechanized Brigade
- 6th Armored Division, with the 12th and 98th Armored Brigades and the 11th Mechanized Brigades
- 7th Mechanized Division, with the 58th and 68th Armored Brigades and the 78th Mechanized Brigade
- 8th Armored Division, which included the 62nd and 65th Armored Brigades and the 32nd Mechanized Brigade
- 9th Armored Division, with the 43rd and 91st Armored Brigades and the 52nd Mechanized Brigade.
Bennett said the 1st Corps also [had] four independent special forces regiments, including two trained for heliborne commando operations against the Israeli signals intelligence & observation posts on Mount Hermon and elsewhere in the Golan Heights.
- 2nd Corps HQ Zabadani, covers north of Damascus, to Homs and includes Lebanon.
- Bennett said in 2001 that the corps' principal units were believed to include:
- 1st Armored Division, with the 44th and 46th Armored Brigades and the 42nd Mechanized Brigade
- 3rd Armored Division, with the 47th and 82nd Armored Brigades and the 132nd Mechanized Brigade
- 11th Armored Division, with the 60th and 67th Armored Brigades and the 87th Mechanized Brigade
- 4th Mechanized Division with the 1st Armored Brigade and the 61st and 89th Mechanized Brigades
- 10th Mechanized Division, headquartered in Shtoura, Lebanon. Its main units [were in 2001] deployed to control the strategic Beirut-Damascus highway with the 123rd Mechanized Brigade near Yanta, the 51st Armored Brigade near Zahle in the Beqaa Valley and the 85th Armored Brigade, deployed around the complex of positions at Dahr al-Baidar.
- three other heavy brigades from the 3rd and 11th Armored Divisions [were] known to be regularly deployed to eastern Lebanon.
- there [were] five special forces regiments in the Lebanon.
- 3rd Corps HQ Aleppo, based in the north and covered Hama, the Turkish and Iraqi borders, the Mediterranean coastline and was tasked with protecting the complex of chemical and biological warfare and missile production and launch facilities.
- The 2nd Reserve Armored Division, with the 14th and 15th Armored Brigades and the 19th Mechanized Brigade. The 2nd [was] also believed to operate as the main armored forces training formation. It seems likely that the "2nd" designation, reported in 2001, was incorrect, as it has not been reported during the Syrian Civil War.
- Other units under the control of this corps included four independent infantry brigades, one border guard brigade, one independent armored regiment, effectively a brigade group, and one special forces regiment.
- the Coastal Defense Brigade, which [operated] largely as an independent unit within the 3rd Corps area, [was] headquartered in the naval base of Latakia with four Coastal Defense Battalions in Latakia, Banias, Hamidieh and Tartus. Each Battalion has four batteries of both the short range SSC-3 Styx and long range SSC-1B Sepal missile systems.
The IISS listed smaller formations in 2006 as:[75]
- Four independent Infantry Brigades
- Ten independent Airborne Special Forces Regiments (Seven regiments attached to 2nd Corps)
- Two independent Artillery Brigades
- Two independent Anti-tank Brigades
- Surface-to-surface Missile Command with three SSM Brigades (each with three SSM battalions),
- Three coastal defense missile brigades
- One brigade with 4 SS-C-1B Sepal launchers,
- One brigade with 6 P-15 Termit launchers, alternative designation SS-C-3 'Styx'
- One brigade with 6+ P-800 Oniks launchers,
- One Border Guard Brigade
Protecting Damascus:
- 4th Mechanized Division (The Defense companies were transformed into the armored division equivalent Unit 569, which in 1984 became the 4th Armored Division.)[76]
- The Republican Guard Armored Division, with three Armored brigades, one Mechanized brigade, and one artillery regiment.
Basic structure until 2011:[77][edit]
- 3 Corps (Falaq): 50,000 men in 3–4 divisions each
- 14 Divisions (Firqa): 5,000–15,000 men in 5–6 brigades/regiments each
- More than 40 Brigades (Liwa): 2,500–3,500 men in 5–6 battalions (1–3 armored/mechanized + artillery/ADA/engineers) each
- Mechanized:
- 105 IFVs in 3 mechanized battalions
- 41 Tanks in 1 armored battalion
- 3,500 soldiers
- Armored:
- 105 Tanks in 3 armored battalions
- 31 IFVs in 1 mechanized battalion
- 2,500 soldiers
- Mechanized:
- More than 20 Regiments (Fawj): 1,500 men
- Light Infantry: 1,500 soldiers in 3 infantry battalions
- Artillery: 45 howitzers and 1,500 soldiers in 3 artillery battalions
- Battalion (Katiba): 300–500 men in 4–5 companies
- Company (Sariya): 60–80 men
Structure in 2022[edit]
Between 2015 and 2018, the Syrian Arab Army underwent many structural changes, with the cooperation of Russia and Iran.[78] As of August 2022, according to Gregory Waters, the structure as the order of battle (at full strength) was:[79][80]
Units reporting to the Chief of Staff[edit]
 Republican Guard
Republican Guard
 4th Armoured Division[81]
4th Armoured Division[81]
- 40th Armored Brigade
- 41st Armored Brigade
- 42nd Armored Brigade
- 138th Mechanized Brigade
- 154th Artillery Regiment
- 555th Special Forces (Airborne) Regiment
- 666th Infantry Regiment (created in 2017)[79]
- 977th Infantry Battalion[79]
- Al-Imam Hussein Brigade[88]
- Harakat Hezbollah al-Nujaba Syrian-wing[89]
Special Forces units formed during the Syrian Civil War:[a]
 25th Special Mission Forces Division[93]
25th Special Mission Forces Division[93]
- 1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th Special Forces (Airborne) Regiments[80]
- Independent Armored Regiment
- Independent Artillery Regiment
1st Corps[edit]
- 5th Mechanized Division
- 15th, 112th and 132nd Mechanized Brigades
- 12th Armored Brigade
- 38th Infantry Brigade[79]
- 175th Artillery Regiment
- 6th Armored Division (formed in 2015)[79]
- 76th and 85th Armored Brigades
- 45th Special Forces Regiment[87]
- 7th Mechanized Division
- 88th, 90th and 121st Mechanized Brigades[87]
- 78th Armored Brigade
- 70th Artillery Brigade
 9th Armored Division
9th Armored Division
 15th Special Forces Division[96]
15th Special Forces Division[96]
- 35th and 127th Special Forces Regiments
- 404th, 405th Armored Regiments
2nd Corps[edit]
- 1st Armored Division
- 61st, 91st and 153rd Armored Brigades
- 57th, 58th and 68th Mechanized Brigades
- 171st Infantry Brigade
- 141st Artillery Regiment
- 167th Anti-Tank Regiment
- 2nd Armored Division (formed in 2015)[79]
- 10th Mechanized Division
- 62nd Mechanized Brigade
- 51st and 58th Armored Brigades[97]
 14th Special Forces Division[98]
14th Special Forces Division[98]
- 36th, 554th and 556th Special Forces Regiments
3rd Corps[edit]
- 3rd Armored Division
- 65th and 81st Armored Brigades
- 21st Mechanized Brigade
- 67th and 155th Artillery Regiments[99]
- 8th Armored Division (formed in 2015)[100]
- 33rd and 47th[101] Armored Brigades
- 45th Mechanized Brigade
- 45th Artillery Regiment
 11th Armored Division[102]
11th Armored Division[102]
 17th Division (HQ Deir ez-Zor)
17th Division (HQ Deir ez-Zor)
- 18th Armoured Division (HQ Aleppo)[106]
- 131st, 134th and 167th Armoured Brigades
- 120th Mechanized Brigade
- 64th Artillery Regiment
 Syrian Border Guard Forces[107]
Syrian Border Guard Forces[107]
- 5th Regiment (Hasakah pocket)
- 6th Regiment (Southern Homs)
- 8th Regiment (Jordan-Syria border)
- 10th Regiment (Iraq-Syria border)
- 11th Regiment (Latakia)
- 12th Regiment (Manbij and Ayn al-Arab)
- Unknown (likely Lebanon-Syria border)
5th Assault Corps[edit]
- 1st Assault Brigade[79]
- 13th Battalion
- 2nd Assault Brigade[108]
- 3rd Assault Brigade[79]
- 4th Assault Brigade[79]
- 5th Assault Brigade[79]
- 1st Infantry Regiment
- 2nd Infantry Regiment
- 6th Assault Brigade[79]
- 79th Infantry Battalion
- 86th Infantry Battalion
- 7th Assault Brigade[79]
- 3rd Infantry Battalion
- 8th Assault Brigade[79]
 al-Quds Brigade[109]
al-Quds Brigade[109]
- 103rd and 148th Artillery Regiments[105][111]
History[edit]
5th Assault Corps, also called the Fifth Legion,[59] is an all-volunteer force, part of Syrian Army involved in the Syrian Civil War fighting against the Syrian opposition, Al-Qaeda in Syria, and ISIS.[112] The Fifth Corps of Volunteers recruits men from over age 18 from across the country "not already eligible for military service or deserters".[113][114][115]
According to Abdullah Soleiman Ali in al-Safir paper, formation of 'Fifth Attack Troop Corps' is the apex point of cooperation among members of Russia–Syria–Iran–Iraq coalition.[116] 5th Corps soldiers are trained, equipped and advised by Russian military personnel since their intervention in 2015.[117] Most main battle tanks of the 5th Assault Corps are modernized Soviet tanks, including the T-62M and T-72B3.[117]
The 5th Corps unit, The Ba'ath Legion, was formed from Ba'ath Brigades volunteers.[118] According to the Russian International Affairs Council, the Qalamoun Shield Forces also joined the Fifth Corps, though no other sources confirmed this.[119]
In February 2018, 20 members[120] of the ISIS Hunters (a 5th Corps subunit)[citation needed] died in a US airstrike.[121][122]
In March 2021, the 5th Corps unit supported by the Russians managed to control Tuenan gas plant and Al-Thawrah oilfield in Raqqa Governorate, previously held by Liwa Fatemiyoun.[123] That month, its commander since January 2018, Major General Zaid Salah (formerly commander the Republican Guard’s 30th Division) was sanctioned by the United Kingdom, who named him as "Responsible for the violent repression of the civilian population by troops under his command, particularly during the increased violence of the Idlib/Hama offensive which began in April 2019."[124]On 30 December 2023, Major General Muhammad al-Daher was named as a commander of the 5th Assault Corps.
Military equipment[edit]
.png/230px-Syrian_Army_tanks_1_(Operation_Damascus_Steel%2C_March_2018).png)

The majority of Syrian military equipment was manufactured by Soviet Union, Russia, China and Iran.[125][126] Military equipment of the Syrian Army as of 2020:[127][128]
- ≈ 5,900 armoured fighting vehicles (including in storage):
- ≈ 2,700 main battle tanks
- ≈ 2,400 infantry fighting vehicles and armored personnel carriers
- ≈ 800 reconnaissance vehicles
- ≈ 2,800 utility vehicles (including in storage):
- ≈ 300 military engineering
- ≈ 2500 logistics and all-terrain vehicles
- ≈ 1,600 mortars
- ≈ 5,130 towed artillery pieces:
- ≈ 2,330 field guns/anti-tank guns/howitzers
- ≈ 2,800 anti-aircraft guns
- ≈ 600 self-propelled artillery pieces:
- ≈ 2,500 anti-tank guided weapon launchers
- ≈ 600 multiple launch rocket systems
- ≈ 100 tactical ballistic missile launchers
- 5,460+ surface-to-air missile launchers:
- 5,000+ MANPADS
- 460+ self-propelled air-defense systems
- ≈ N/A unmanned aerial vehicles
- ≈ N/A super-sonic cruise missiles
Uniforms, weapons and rank insignia[edit]
Uniforms and personnel equipment[edit]
Service uniforms for Syrian officers generally follow the British Army style, although army combat clothing follows the Soviet model.[129] Each uniform has two coats: a long one for dress and a short jacket for informal wear. Army officer uniforms are khaki in summer, olive in winter. All Army (including paratroops and special forces) and Air Defense Force personnel wear camouflage uniforms.[130] Among the camouflage are Red Lizard, Syrian Leaf patterns, EMR Desert; a locally-made copies of the ERDL and M81 Woodland.[131][130]
Officers have a variety of headgear, including a service cap, garrison cap, and beret (linen in summer and wool in winter).[131] The color of the beret varies according to the officer's unit. The most common beret color is black, for Infantry, Engineering, Signals and supporting arms personnel, followed by green, for Armored, Mechanized and Artillery personnel, red for the Republican Guard and Military Police, and maroon (blue) for the Special Forces.[132]
Since 2009, the SAA had acquired large numbers of Chinese-produced combat gear, including helmets and bullet proof vests.[130] In 2011, the standard issue combat helmets were the olive Chinese QGF-02, and the Soviet SSh-68 for the reserve forces.[133] Both of them can be equipped with the Syrian Leaf camouflage helmet covers. Since 2015, some regular units were equipped with 6B7 helmets from Russia. Standard protective gear for all Army units were (PASGT) TAT-BA-7 bullet-proof vests. The Republican Guard and Special Forces were the only units equipped with ACH, FAST, 6B47 helmets and 6B45, Ruyin-3 ballistic vests. The Syrian military also provides NBC uniforms to soldiers to remain effective in an environment affected by biological or chemical agents. This uniform consists of a Russian-made Model GP-5, PMK and ShMS-41 masks.[134]
Service weapons[edit]
Service weapons of the Syrian Arab Army consist of stocks of Cold War-era arms. Main service pistols of the Syrian Army are Makarov PM and Stechkin-APS. Main service assault rifles are Soviet AKM/AKMS, AK-74, Chinese Type 56 and Sa vz. 58.[135] Main service carbines are AKS-74U and copies of Belgian FN FAL. Syrian Army uses the Dragunov SVD sniper rifles and derivatives like the Tabuk, PSL. Army has also modern snipers like Steyr SSG 69,[136] Heckler & Koch G3 and Syrian-made Golan S-01.[137] The most widely used machine guns are RPK, PKM, Type 73,[138] NSV and PKP Pecheneg.[139] Until 2011, the procurement of large numbers of AK-74Ms was planned to replace the AK(M) and other derivatives, the Civil War put a halt to this large scale re-equipment programme.[130] Since 2015, Syrians have received big equipment assistance from Russia.[140]
Ranks[edit]
The rank insignia of commissioned officers.[129]
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | Officer cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
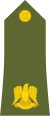
|

|

|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| فريق Fariq |
عماد أول Eimad 'awal |
عماد Eimad |
لواء Alliwa' |
عميد Amid |
عقيد Aqid |
مقدم Muqaddam |
رائد Ra'id |
نقيب Naqib |
ملازم أول Mulazim awwal |
ملازم Mulazim |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The rank insignia of non-commissioned officers and enlisted personnel.[129]
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| مساعد أول Musaeid 'awal |
مساعد ثاني Musaeid thani |
مساعد Musaeid |
رقيب أول Raqib 'awal |
رقيب ثاني Raqib thani |
رقيب Raqib |
عريف Earif |
جندي أول Jundiun 'awal |
جندي Jundiun | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Awards[edit]
Although some twenty-five orders and medals are authorized, generally only senior officers and warrant officers wear medal ribbons. The following are some important Syrian awards: Order of Umayyad, Medal of Military Honor, the War Medal, Medal for Courage, Yarmuk Medal, Wounded in Action Medal, and Medal of 8 March 1963.[129]
Chief of the General Staff of the Army[edit]
The Chief of the General Staff of the Army and Armed Forces (Arabic: رئيس هيئة الأركان العامة للجيش والقوات المسلحة, romanized: Rayiys hayyat al'arkan aleamat liljaysh walquaat almusalaha) is the professional head of the Syrian Armed Forces and the Syrian Army. The Chief of the General Staff is appointed by the President of Syria, who is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces.[142] As of 2023, the Chief of the General Staff has been Lt. Gen. Abdul Karim Mahmoud Ibrahim, who was appointed to the role by Syrian President Bashar Al-Assad.[143] In April 2022, Maj. Gen. Mufid Hassan was also appointed as the Deputy Chief of the General Staff.[70]
References[edit]
![]() This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Country Studies. Federal Research Division.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Country Studies. Federal Research Division.
- ^ Syria News 1 August 2013, President Bashar Al-Assad visits soldiers to mark Army Day and pledge victory. 3 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24. Retrieved 2015-10-12 – via YouTube.
- ^ The Military Balance 2023 page 354
- ^ "The World Factbook". cia.gov. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
- ^ "CIA World Factbook". CIA. Archived from the original on 2016-03-22. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 447.
- ^ Bou-Nacklie, N. E. “Les Troupes Speciales: Religious and Ethnic Recruitment, 1916-46.” International Journal of Middle East Studies, vol. 25, no. 4, Cambridge University Press, 1993, pp. 645–60, http://www.jstor.org/stable/164539 Archived 2022-01-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Morris, Benny (2008), 1948: A History of the First Arab–Israeli War, p. 251. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-15112-1.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 448.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 457–458.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 458.
- ^ Vanly, I. C. (1992). "The Kurds in Syria and Lebanon". In Kreyenbroek, P. G.; Sperl, S. (eds.). The Kurds: A Contemporary Overview. Routledge. pp. 151–2. ISBN 0-415-07265-4.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 459–460.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 464.
- ^ Hanna Batatu (1999). Syria's Peasantry, the Descendants of Its Lesser Rural Notables, and Their Politics. Princeton University Press. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-691-00254-5. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- ^ Samuel M. Katz, Arab Armies of the Middle East Wars, Osprey Publishing Men-at-Arms 194, 1988, 13.
- ^ Pollack 2002, p. 476–478.
- ^ British documents, sealed for 30 years, now reveal that Hussein sent “a series of messages” to the British Embassy in Amman
- ^ An order of battle of the Syrian Army in October 1973 can be found in Colonel Trevor Dupuy, Elusive Victory: The Arab–Israeli Wars 1947–74, MacDonald and Jane's, London, 1978
- ^ Patrick Seale, Asad: The Struggle for the Middle East (London: I.B. Tauris & Co, 1988), p.327, via Holliday 2013, 12.
- ^ Nikolaos van Dam, The Struggle for Power in Syria: Politics and Society under Asad and the Ba'th Party, (New York: I.B. Tauris & Co Ltd, 2011), p.114, via Holliday 2013, 12.
- ^ van Dam, 2011, p.104, via Holliday 2013.
- ^ a b "Syria's Praetorian Guards: A Primer". Middle East Intelligence Bulletin. Vol. 2 No. 7 (5 August 2000). Archived from the original on 2012-07-04. Retrieved 20 May 2011.
- ^ a b "Is the Syrian Army Falling Apart?". matthewaid.com. Archived from the original on 2014-01-16. Retrieved 2012-03-16.
- ^ Cooper 2015, p. 13.
- ^ Near East and South Asia Analysis, p27.
- ^ Norman Schwarzkopf, It Doesn't Take A Hero, Bantam Books, 1993, 467–69.
- ^ Nicholas Blandford, "Syria reduced troop strength in Lebanon," Jane's Defence Weekly, 29 September 2004, 31.
- ^ IISS 2010, p. 272–273.
- ^ IISS 2011, p. 330.
- ^ a b International Institute for Strategic Studies, The Military Balance 2010, 272–273.
- ^ a b c "Syria's diminished security forces". Agence France-Presse. 27 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Syrian defections hurt army morale". Independent Online (South Africa). 5 July 2012. Archived from the original on 2013-12-09. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ Security, Global. "Syrian Army equipment".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-02-02. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Over 10,000 soldiers have deserted Syria army, says high-ranking defector". Haaretz. Reuters and Deutsche Presse-Agentur. 1 October 2011. Archived from the original on 2013-11-16. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ Atassi, Basma (16 November 2011). "Free Syrian Army grows in influence". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 2014-01-17. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "Free Syrian Army soldier: "We lack weapons"". France 24. 18 November 2011. Archived from the original on 2013-10-20. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ "Syria's army weakened by growing desertions". Reuters. 1 January 2012. Archived from the original on 2015-10-01. Retrieved 2017-07-02.
- ^ Emre, Peker; Abu-Nasr, Donna (15 March 2012). "Syrian Armed Forces Desertion Said to Surge to 60,000". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ "Chief of protocol at the Syrian presidential palace denies defection". Al Arabiya. 9 August 2012. Archived from the original on 9 August 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2012.
- ^ "Dozens of Syrian officers defect to Turkey as Russia warns against arming rebels". Haaretz. 14 June 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-06-15. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
- ^ Wikstrom, Cajsa (9 February 2011). "Syria: 'A kingdom of silence'". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 29 May 2023.
- ^ Holliday, 2013, 11, 12.
- ^ a b Lister, Charles (May 2014). "DYNAMIC STALEMATE: SURVEYING SYRIA'S MILITARY LANDSCAPE" (PDF). Brookings Doha Center.
- ^ "DEFECTED GENERAL: 'DRUZE DO NOT REPRESENT A COG IN THE REGIME MACHINE'". Syria Direct. 30 March 2015. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ^ Sherlock, Ruth (7 April 2015). "In Syria's war, Alawites pay heavy price for loyalty to Bashar al-Assad". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 2015-04-07. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ^ "Israel sees Syrian army growing beyond pre-civil war size". DefenceWeb. Reuters. 8 August 2018. Archived from the original on 11 January 2019. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- ^ Holliday 2013, 26, citing "By All Means Necessary: Individual and Command Responsibility for Crimes against Humanity in Syria," Human Rights Watch, December 2011, p. 36; Syrian Observatory for Human Rights Facebook page Archived 2014-03-13 at the Wayback Machine, January 24, 2012; Syrian Revolution Coordinator's Union Facebook page Archived 2012-07-18 at the Wayback Machine, February 7, 2012; Local Coordination Committees website Archived 2013-04-10 at the Wayback Machine, November 15, 2012.
- ^ "Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 1151/2011 of 14 November 2011 implementing Regulation (EU) No 442/2011 concerning restrictive measures in view of the situation in Syria" (PDF). Official Journal of the European Union. 15 November 2011. Archived from the original on 2013-05-22. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- ^ Boyd, Henry (12 March 2012). "Shades of Hama and Grozny in Homs and Idlib". International Institute for Strategic Studies. Archived from the original on 2012-06-27. Retrieved 2012-08-11.
- ^ Holliday, 2013, 42, 46, 47. Holliday's sources include "Skype Interview with exiled former Syrian Army General Officer in Washington, DC on April 19, 2012."
- ^ Holliday, 2013, 33, citing "Clashes between Syrian troops and army defectors kill at least 13," Washington Post, October 13, 2011; Syrian Revolution Coordinator's Union Facebook Page <facebook.com/monasiqoon>, November 13, 2012.
- ^ Alice Martins, Watching Rebels Fight Among Themselves for the City of Raqqa Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine, SyriaDeeply.org Beta, October 2, 2013.
- ^ news24.com
- ^ Iran's Secret Army. YouTube. 22 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2016-01-02. Retrieved 2015-10-12.
- ^ "Insight: Battered by war, Syrian army creates its own replacement". Reuters. 21 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-06-01. Retrieved 2017-07-02.
- ^ "ماهو الفيلق الرابع اقتحام الذي بدأ عملياته في ادلب و ماهي مهامه؟ - وكالة أوقات الشام الإخبارية". shaamtimes. Archived from the original on 2 September 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g Pesach Malovany; Nehemiah Burgin (16 February 2018). "Mother Russia Holds the Reigns[sic]". Israel Defense (Arrowmedia). Archived from the original on 2018-02-19. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^ a b "The Fifth Legion: A New Auxiliary Force - Syria Comment". 24 December 2016. Archived from the original on 2018-08-13. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- ^ a b c "Streitkräfte des Assad-Regimes, Februar 2017" [Armed forces of the Assad regime, February 2017] (PDF). Truppendienst.com (Austrian Armed Forces) (in German). 15 February 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-02-04. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- ^ a b Abdulrahman al-Masri (11 January 2017). "Analysis: The Fifth Corps and the State of the Syrian Army". Syria Deeply. Archived from the original on 2018-02-04. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- ^ Nidal Hmadeh (19 August 2015). "The Syrian 4th Regiment...the Full Story". al-Ahed News. Archived from the original on 2018-02-04. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- ^ a b Kheder Khaddour (14 March 2016). "Strength in Weakness: The Syrian Army's Accidental Resilience". Carnegie Middle East Center. Archived from the original on 2018-02-08. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- ^ Sylvia Westall; Tom Perry (8 October 2015). "Syria extends offensive to retake territory in west". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2018-02-19. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^ Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi (24 December 2016). "The Fifth Legion: A New Auxiliary Force". Syria Comment. Archived from the original on 2018-02-20. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^ Waters, Gregory (November 17, 2018). "The +20 men killed near Sirmaniyah reportedly belonged to the 6th Division, one of two divisions created under the Russian-built 4th Corps back in 2015. The 4th Corps project largely failed & the 6th & 2nd Divisions have remained in Latakia since".
- ^ Potter, Lawrence G. (2014). Sectarian Politics in the Persian Gulf. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 36. ISBN 978-0199377268.
- ^ Chris Tomson (6 April 2016). "Strategic town of Al-Eis recaptured during night raid led by Iranian troops - Map update". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 9 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- ^ Thanassis Cambanis (5 November 2015). "Assad's Sunni Foot Soldiers". Foreign Policy.
- ^ a b Lund, Aron (2022-05-23). "Can Assad's New Military Appointments Help Rebuild His Regime?". The Century Foundation. Retrieved 2023-04-07.
- ^ "Pro-regime Sunni fighters in Aleppo defy sectarian narrative - Al-Monitor: the Pulse of the Middle East". Al-Monitor. 14 March 2014.
- ^ Ripley, Tim (2017). Syrian army prepares for post-conflict challenges. Janes´s. p. 4.
- ^ Richard M. Bennett, The Syrian Military: A Primer Archived 2012-06-29 at the Wayback Machine, Middle East Intelligence Bulletin, August/September 2001.
- ^ Library of Congress Country Study Syria
- ^ International Institute for Strategic Studies, The Military Balance 2006, p.208-9
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-03-08. Retrieved 2012-04-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "The Syrian Army Doctrinal Order of Battle" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-11-01. Retrieved 2013-12-30.
- ^ Eden Kaduri, Yehoshua Kalisky, Tal Avraham (6 September 2023). "Rebuilding the Syrian Military: The Threat to Israel". INSS Tel Aviv University. Retrieved 25 November 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Gregory Waters (18 July 2019). "The Lion and The Eagle: The Syrian Arab Army's Destruction and Rebirth". Middle East Institute. Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ^ a b c Gregory Waters (12 September 2022). "From Tiger Forces to the 16th Brigade: Russia's evolving Syrian proxies". Middle East Institute. Retrieved 16 November 2023.
- ^ a b c Syria - The Special Forces and the Elite Units
- ^ Leith Fadel (23 November 2016). "Four high-ranking jihadist commanders killed in Aleppo". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2017-02-16. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ Loveday Morris (22 January 2013). "Assad's Lionesses: the female last line in the battle for Syria". The Independent. Retrieved 21 September 2023.
- ^ Sarah Leduc (2 April 2015). "Assad's female fighters: Progress or propaganda?". France 24. Retrieved 18 November 2023.
- ^ "Arab armies turn to women: An illusion or a new reality?". The New Arab. 17 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- ^ Paul Antonopoulos (22 January 2017). "New Syrian Arab Army Division established in preparation of new offensive". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ a b c d e f Gregory Waters (12 May 2020). "Current Syrian Army Deployments". International Review. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ^ Tal Beeri (27 July 2023). "The "Al-Imam Hussein Brigade"- The Assimilation of a Shiite Militia into The Syrian Army's 4th Division, As Well as its Attacks on Israeli and US forces". Israel Alma. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- ^ "Harakat al-Nujaba': Interview". 5 September 2018.
- ^ "Syria's Elite Military Units: Keys to Stability and Succession" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 1 July 2022.
- ^ Harris, William (2018). "Glossary". Quicksilver War: Syria, Iraq and the Spiral of Conflict. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 183. ISBN 9780190874872.
- ^ "Return to the northeast: Syrian Army deployments against Turkish forces". Middle East Institute.
- ^ "Tiger Forces renamed and placed under command of Syrian Army". Al-Masdar News. 29 August 2019. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ "Largest Syrian Brigade Nears Breaking Point". Arutz Sheva. 16 May 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-06-07. Retrieved 2013-06-07.
- ^ Fadel, Leith (12 September 2016). "Syrian Army restores all lost points in Golan Heights". Archived from the original on 2016-09-13. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ^ "Syrian Army kicks off new operation in Daraa". May 8, 2020. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2023.
- ^ Joseph Holliday, 'The Assad Regime: From Counterinsurgency to Civil War,' Institute for the Study of War, March 2013. Seemingly the best concise description and analysis of the Syrian Army and its involvement in the current Syrian Civil War.
- ^ "Confirmed: Syrian Army's full order of battle for east Damascus offensive". Al-Masdar News. 18 February 2018. Archived from the original on 13 May 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ a b Cooper 2015, p. 18.
- ^ Understanding Syria’s Military Deployments in Idlib
- ^ Leith Fadel (22 March 2017). "Syrian Army reinforcements arrive to northern Hama to fend off jihadist offensive". al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 22 March 2017.
- ^ "Syria's Nusra seizes tanks, APCs from Assad's army". Middle East Eye. December 20, 2014. Retrieved December 20, 2014.
- ^ "Syrian commandos begin long campaign to Jisr Al-Shughour". 20 February 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-04-30. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- ^ Gregory Waters (20 November 2019). "Return to the northeast: Syrian Army deployments against Turkish forces". Middle East Institute. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ a b Gregory Waters (20 November 2019). "Return to the northeast: Syrian Army deployments against Turkish forces". Middle East Institute. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ Cooper 2015, p. 13, 18-19.
- ^ Gregory Waters. "Syria's Border Guards: From Auxiliary to Frontlines". Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- ^ Understanding Syria’s Military Deployments in Idlib
- ^ a b Al-Jabassini, Abdullah (2019). From Insurgents to Soldiers: The Fifth Assault Corps in Daraa, Southern Syria. Wartime and Post-Conflict in Syria. European University Institute. ISBN 978-92-9084-767-0.
- ^ "The Palestinian al-Quds Brigade has a new Iran-backed militia for fighting in Aleppo". Al-Dorar al-Shamia. 20 June 2017. Archived from the original on 25 August 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ Игорь Январёв, Никита Голобоков (2019-04-20). "Как Россия меняет Сирийскую армию". Archived from the original on 2020-02-28. Retrieved 2020-02-28.
- ^ "Syrian army forms volunteer corps to fight militants". Reuters. 22 November 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-12-04. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ^ "Syria launches new commando force as war heats up". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-07. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- ^ "The Fifth Legion: A New Auxiliary Force". 24 December 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-12-25. Retrieved 2016-12-24.
- ^ وزارة الدفاع في الجمهورية العربية السورية (30 January 2017). "شاهد رمايات مدفعية الجيش العربي السوري على إرهابيي داعش شرقي حمص وتحرير الكتيبة المهجورة الثالثة". Archived from the original on 2017-01-30. Retrieved 2017-01-30 – via YouTube.
- ^ Staff writers. "Fifth Attack Troops Corps entered the Syria civil war". mashreghnews (in Persian). Archived from the original on 2016-12-07. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- ^ a b Leith Fadel (11 August 2017). "Pictures of Syrian Army units that will lift Deir Ezzor seige [sic]". Al-Masdar News. Archived from the original on 2017-08-11. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- ^ "Syrian regime forms militia mostly from the ruling party". Zaman Alwasl. 16 March 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-03-17. Retrieved 17 March 2017.
- ^ Mona Alami (6 March 2019). "Can Assad's Demobilization, Demilitarization, and Rehabilitation Strategy Actually Consolidate Syria's Paramilitary Forces?". Washington Institute. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- ^ "Pro-gov't ISIS Hunters release official statement after US airstrikes in Deir Ezzor". 11 February 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-02-12. Retrieved 2018-02-11.
- ^ "US-led coalition strikes kill pro-regime forces in Syria". 7 February 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-04-30. Retrieved 2018-02-11.
- ^ "Inside the U.S. Coalition attack on Syrian forces in Deir Ez Zor". 10 February 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-02-12. Retrieved 2018-02-11.
- ^ "بعد حقل توينان.. القوات الروسية تبسط سيطرتها على حقل الثورة النفطي وفاطميون تنسحب". eyeofeuphrates.com (in Arabic). 13 March 2021.
- ^ "New UK sanctions targeting Assad regime for repressing the Syrian people". GOV.UK. 2021-03-15. Retrieved 2022-09-14.
- ^ Security, Global. "Syrian Army equipment".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-02-02. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Nine Years of War — Documenting Syrian Arab Army's Armored Vehicles Losses". bellingcat. 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2022-12-08.
- ^ ANALYSIS - Missile landscape of the Syrian war
- ^ a b c d "Uniforms and Rank Insignia". Library of Congress. April 1987. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
- ^ a b c d Stijn Mitzer and Joost Oliemans (6 November 2016). "Photo Report: The Syrian Arab Army (1)". Oryx Blog. Retrieved 12 October 2023.
- ^ a b "A snapshot of camouflage patterns in Syria – Armament Research Services". 15 August 2016. Retrieved 2020-09-02.
- ^ "From Russia with Love, Syria's AK-74Ms". bellingcat. 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Syria Ssh68". Brendon's Helmets. Archived from the original on 2013-03-30. Retrieved 2013-07-12.
- ^ Gordon Rottman (27 May 1993). Armies of the Gulf War. Osprey Publishing. p. 58. ISBN 978-1-85532-277-6. Archived from the original on 22 April 2014. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ^ "Syrie: les ISIS Hunters, ces soldats du régime de Damas formés par la Russie". France-Soir (in French). 30 May 2017. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- ^ Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (January 27, 2009). ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- ^ "La 104ème brigade de la Garde républicaine syrienne, troupe d'élite et étendard du régime de Damas". France-Soir (in French). 20 March 2017. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 4 September 2018.
- ^ Richter, Ali (16 March 2016). "North Korean Type 73 GPMGs in Iraq, Syria & Yemen". armamentresearch.com.
- ^ "Syrian army general's weapons request". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 8 September 2017.
- ^ "From Russia with Love, Syria's AK-74Ms". 19 February 2015. Archived from the original on 2019-02-06. Retrieved 2017-11-03.
- ^ a b "شعار الرأس" [Main logo]. mod.gov.sy (in Arabic). Ministry of Defence (Syria). Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ O. Peri and H. Varulkar (23 September 2019). "Struggle Between Russia, Iran For Control Over Syria's Centers Of Power". Iran, Russia, Syria Inquiry & Analysis Series. 1475.
- ^ "Assad Appoints Pro-Russia General as Chief of Staff". The Syrian Observer. Zaman Al Wasl. 19 April 2019.
- ^ "Special Forces" in the Syrian Arab Army denotes specialized "light" infantry (airborne, air assault) and are "elite" only in relation to the conventional mechanized, armored units of the SAA. According to a declassified CIA report the stated Special Forces regiments were created to conduct counter-insurgency operations.[90] Special Forces units included the: 41st, 45th, 46th, 47th, 53rd and 54th independent special forces regiments.[91] Special Forces were heavily used from the early stage of the Syrian Civil War and as a result suffered heavy casualties, possibly up to three regiments (41st, 46th, 54th) may have been destroyed during the Syrian Civil War, the surviving three regiments were merged to other formations such as the Republican Guard, Tiger Forces and 4th Corps.[79] Later reports state that two battalions from the 54th regiment serve within the 17th Division.[92]
Notes[edit]
- Richard M. Bennett, The Syrian Military: A Primer, Middle East Intelligence Bulletin, August/September 2001.
- Cooper, Tom (2015). Syrian Conflagration: The Civil War 2011-2013. Middle East@War Volume 1. Helion & Co. ISBN 978-1-910294-10-9.[1]
- Joseph Holliday, 'The Assad Regime: From Counterinsurgency to Civil War,' Institute for the Study of War, March 2013. The best concise description and analysis of the Syrian Army and its involvement in the current Syrian Civil War until Cooper 2015.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2010). The Military Balance 2010. London, United Kingdom: Routledge / IISS. ISBN 978-1857435573.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2011). The Military Balance 2011. Routledge. pp. 311–312. ISBN 978-1-85743-606-8.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2019). "The Military Balance 2019". Military Balance. London: Routledge. doi:10.1080/04597222.2018.1561033. ISSN 1479-9022. S2CID 219628874.
- Pollack, Kenneth M. (2002). Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness 1948–91. Lincoln and London: University of Nebraska Press. Reviewed in Brooks, Risa A. "Making Military Might: Why Do States Fail and Succeed? A Review Essay." International Security 28, no. 2 (Fall 2003): 149-191.
Further reading[edit]
- Department of the Army, Area Handbook for Syria, Washington, For sale by the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Govt. Print. Off., 1965, "Department of the Army pamphlet no. 550-47." Revision of the 1958 edition.
- Pesach Melovany, Out of the North an Evil shall break forth, Tel-Aviv: Contento de Semrik, 2014.
- Hicham Bou Nassif, 'Second Class: the Grievances of Sunni Officers in the Syrian Armed Forces'
- History of the Syrian Arab Army: Prussianization of the Arab Army, the Arab Revolt of 1916–1918, and the cult of nationalization of Arabs in the Levant after World War I, Infantry Magazine, Nov-Dec 2005.
- General Mustafa Tlas (ed.), History of the Syrian Arab Army/Al-Tareekh Al-Jaish Al-Arabi Al-Soori, Volume 1: 1901–1948, Center for Military Studies. Damascus, 2000. Volume 1 is 568 pages long and covers the Arab Revolt, the short-lived monarchy under King Feisal bin Hussein, the French Mandate, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and finally Syrian independence in 1949.

